Useful Information
What is Packing ?
Packaging is the technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of design, evaluation, and production of packages. Packaging can be described as a coordinated system of preparing goods for transport, warehousing, logistics, sale, and end use. Packaging contains, protects, preserves, transports, informs, and sells. In many countries it is fully integrated into government, business, institutional, industrial, and personal use.
Package labeling or labelling is any written, electronic, or graphic communication on the package or on a separate but associated label.
As of 2003, the packaging sector accounted for about two percent of the gross national product in developed countries. About half of this market was related to food packaging.
Packaging and package labeling have several objectives
- Physical protection – The objects enclosed in the package may require protection from, among other things, mechanical shock, vibration, electrostatic discharge, compression, temperature etc.
- Barrier protection – A barrier from oxygen, water vapor, dust, etc., is often required. Permeation is a critical factor in design. Some packages contain desiccants or oxygen absorbers to help extend shelf life. Modified atmospheres or controlled atmospheres are also maintained in some food packages
- Containment or agglomeration – Small objects are typically grouped together in one package for reasons of efficiency. Liquids, powders, and granular materials need containment.
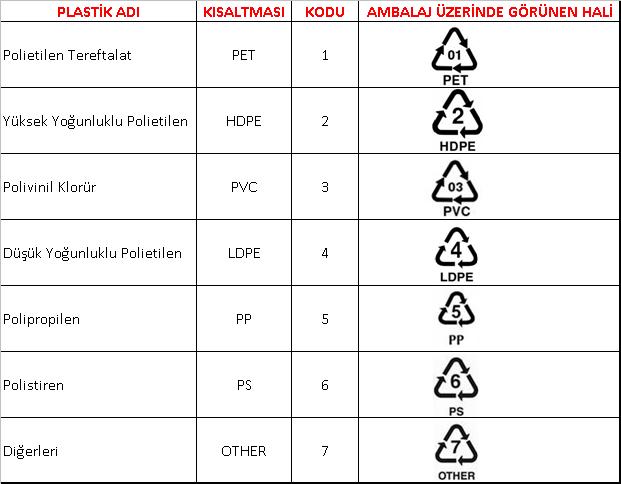
- Information transmission – Packages and labels communicate how to use, transport, recycle, or dispose of the package or product. With pharmaceuticals, food, medical, and chemical products, some types of information are required by governments. Some packages and labels also are used for track and trace purposes. Packages may indicate their material with a symbol.
- Marketing – The packaging and labels can be used by marketers to encourage potential buyers to purchase the product. Package graphic design and physical design have been important and constantly evolving phenomenon for several decades. Marketing communications and graphic design are applied to the surface of the package and (in many cases) the point of sale display. Most packaging is designed to reflect the brand's message and identity.
- Security – Packaging can play an important role in reducing the security risks of shipment. Packages can be made with improved tamper resistance to deter tampering and also can have tamper-evident features to help indicate tampering. Packages may include authentication seals and use security printing to help indicate that the package and contents are not counterfeit. Packages also can include anti-theft devices, such as dye-packs, or electronic article surveillance tags that can be activated or detected by devices at exit points and require specialized tools to deactivate. Using packaging in this way is a means of loss prevention.
- Convenience – Packages can have features that add convenience in distribution, handling, stacking, display, sale, opening, reclosing, use, dispensing, reuse, recycling, and ease of disposal
- Portion control – Single serving or single dosage packaging has a precise amount of contents to control usage. Bulk commodities (such as salt) can be divided into packages that are a more suitable size for individual households. It also aids the control of inventory: selling sealed one-liter-bottles of milk, rather than having people bring their own bottles to fill themselves.
Polyethylene terephthalate (sometimes written poly(ethylene terephthalate)), commonly abbreviated PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P, is a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in synthetic fibers; beverage, food and other liquid containers; thermoforming applications; and engineering resins often in combination with glass fiber. It may also be referred to by the brand name Dacron; in Britain, Terylene; or, in Russia and the former Soviet Union, Lavsan.
The majority of the world's PET production is for synthetic fibers (in excess of 60%), with bottle production accounting for about 30% of global demand. In the context of textile applications, PET is referred to by its common name, polyester, whereas the acronym PET is generally used in relation to packaging. Polyester makes up about 18% of world polymer production and is the third-most-produced polymer; polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are first and second, respectively.
PET consists of polymerized units of the monomer ethylene terephthalate, with repeating C10H8O4 units. PET is commonly recycled, and has the number 1 as its recycling symbol. Biaxially oriented PET film (often known by one of its trade names, "Mylar") can be aluminized by evaporating a thin film of metal onto it to reduce its permeability, and to make it reflective and opaque (MPET).
PET was patented in 1941 by John Rex Whinfield, James Tennant Dickson and their employer the Calico Printers' Association of Manchester, England. E. I. DuPont de Nemours in Delaware, USA, first used the trademark Mylar in June 1951 and received registration of it in 1952. It is still the best-known name used for polyester film. The current owner of the trademark is DuPont Teijin Films US, a partnership with a Japanese company.
In the Soviet Union, PET was first manufactured in the laboratories of the Institute of High-Molecular Compounds of the USSR Academy of Sciences in 1949, and its name "Lavsan" is an acronym thereof (лаборатории Института высокомолекулярных соединений Академии наук СССР).
The PET bottle was patented in 1973 by Nathaniel Wyeth.
***
Polyvinyl chloride, more correctly but unusually poly(vinyl chloride), commonly abbreviated PVC, is the third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer, after polyethylene and polypropylene.
PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible. The rigid form of PVC is used in construction for pipe and in profile applications such as doors and windows. It is also used for bottles, other non-food packaging, and cards (such as bank or membership cards). It can be made softer and more flexible by the addition of plasticizers, the most widely used being phthalates. In this form, it is also used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, imitation leather, signage, inflatable products, and many applications where it replaces rubber.
PVC was accidentally synthesized in 1872 by German chemist Eugen Baumann. The polymer appeared as a white solid inside a flask of vinyl chloride that had been left exposed to sunlight. In the early 20th century the Russian chemist Ivan Ostromislensky and Fritz Klatte of the German chemical company Griesheim-Elektron both attempted to use PVC in commercial products, but difficulties in processing the rigid, sometimes brittle polymer thwarted their efforts. Waldo Semon and the B.F. Goodrich Company developed a method in 1926 to plasticize PVC by blending it with various additives. The result was a more flexible and more easily processed material that soon achieved widespread commercial use.
***
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging and labeling, textiles (e.g., ropes, thermal underwear and carpets), stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes. An addition polymer made from the monomer propylene, it is rugged and unusually resistant to many chemical solvents, bases and acids.
In 2008, the global market for polypropylene had a volume of 45.1 million metric tons, which led to a turnover of about $65 billion.
When polypropylene film is extruded and stretched in both the machine direction and across machine direction it is called biaxially oriented polypropylene - BOPP. Biaxial orientation increases strength and clarity. BOPP is widely used as a packaging material for packaging products such as snack foods, fresh produce and confectionery. It is easy to coat, print and laminate to give the required appearance and properties for use as a packaging material. This process is normally called converting. It is normally produced in large rolls which are slit on slitting machines into smaller rolls for use on packaging machines.
***
Polyethylene (abbreviated PE) or polythene (IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most common plastic. The annual global production is approximately 80 million tonnes. Its primary use is in packaging (plastic bag, plastic films, geomembranes, containers including bottles, etc.). Thus PE is usually a mixture of similar organic compounds that differ in terms of the value of n.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) - is defined by a density of greater or equal to 0.941 g/cm3. HDPE has a low degree of branching and thus low intermolecular forces and tensile strength. HDPE can be produced by chromium/silica catalysts, Ziegler-Natta catalysts or metallocene catalysts. The lack of branching is ensured by an appropriate choice of catalyst (for example, chromium catalysts or Ziegler-Natta catalysts) and reaction conditions. HDPE is used in products and packaging such as milk jugs, detergent bottles, butter tubs, garbage containers and water pipes. One third of all toys are manufactured from HDPE. In 2007 the global HDPE consumption reached a volume of more than 30 million tons.
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE is defined by a density range of 0.910–0.940 g/cm3. LDPE has a high degree of short and long chain branching, which means that the chains do not pack into the crystal structure as well. It has, therefore, less strong intermolecular forces as the instantaneous-dipole induced-dipole attraction is less. This results in a lower tensile strength and increased ductility. LDPE is created by free radical polymerization. The high degree of branching with long chains gives molten LDPE unique and desirable flow properties. LDPE is used for both rigid containers and plastic film applications such as plastic bags and film wrap. In 2009 the global LDPE market had a volume of about US$22.2 billion (€15.9 billion)
Polycarbonates (PC), known by the trademarked names Lexan, Makrolon, Makroclear, arcoPlus® and others, are a particular group of thermoplastic polymers. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code and are identified as Other, 7. Items made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A(BPA).

 Türkçe
Türkçe  English
English Russian
Russian



